Bookkeeping
Allowance Method for Uncollectible Accounts
However, several other analysis techniques can provide insight regarding the accuracy of prior estimates and the effectiveness of the estimation process. When it comes to bad debt and ADA, there are a few scenarios you may need to record in your books. Doubtful debt is money you predict will turn into bad debt, but there’s still a chance you will receive the money. Remember that writing off an account does not necessarily mean giving up on receiving payment.
Free Course: Understanding Financial Statements
The income statement method (also known as thepercentage of sales method) estimates bad debt expenses based onthe assumption that at the end of the period, a certain percentageof sales during the period will not be collected. The estimation istypically based on credit sales only, not total sales (whichinclude cash sales). In this example, assume that any credit cardsales that are uncollectible are the responsibility of the creditcard company. It may be obvious intuitively, but, by definition, acash sale cannot become a bad debt, assuming that the cash paymentdid not entail counterfeit currency. The income statement method isa simple method for calculating bad debt, but it may be moreimprecise than other measures because it does not consider how longa debt has been outstanding and the role that plays in debtrecovery. The estimation is typically based on credit sales only, not total sales (which include cash sales).
- Instead of the bad debt reserve calculation, companies may use the allowance method, which anticipates that some of a company’s existing debt will be uncollectible and accounts for that prediction right away.
- It is crucial for accounting professionals to use all available tools to understand the effectiveness of past estimates and maintain the confidence of financial statement users in the stated net receivables.
- As of January 1, 2018, GAAP requires a change in how health-careentities record bad debt expense.
Accounting Ratios
In some cases, the company may still pursue collection through a collection agency, legal action, or other means. The customer who filed for bankruptcy on August 3 manages to pay the company back the amount owed on September 10. The company would then reinstate the account that was initially written off on August 3. Explore the role of FASB in financial reporting, including its mission, standards, and collaboration for consistency in accounting practices. Bench simplifies your small business accounting by combining intuitive software that automates the busywork with real, professional human support.
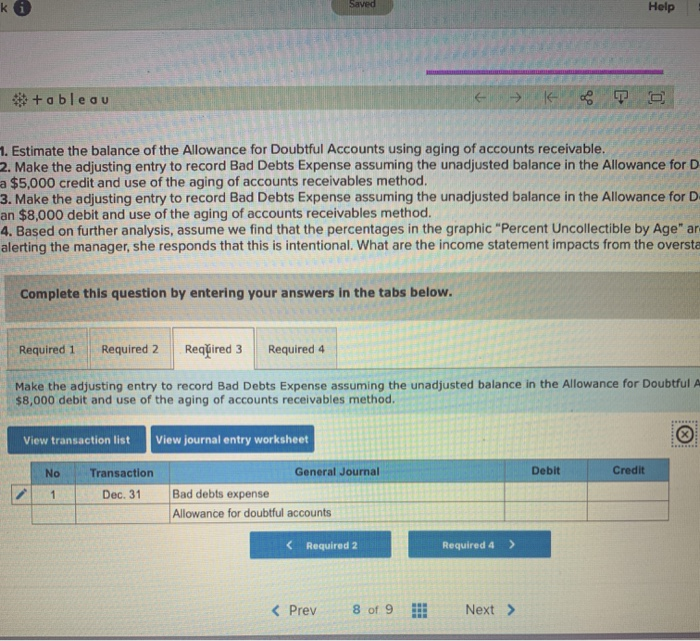
What is the Journal Entry for Uncollectible Accounts?
Debit your Bad Debts Expense account $1,200 and credit your Allowance for Doubtful Accounts $1,200 for the estimated default payments. Use the percentage of bad debts you had in the previous accounting period to help determine your bad debt reserve. Using the example above, let’s say that a company reports an accounts receivable debit balance of $1,000,000 on June 30. The company anticipates that some customers will not be able to pay the full amount and estimates that $50,000 will not be converted to cash. Additionally, the allowance for doubtful accounts in June starts with a balance of zero.
At the end of an accounting period, the Allowance for DoubtfulAccounts reduces the Accounts Receivable to produce Net AccountsReceivable. Note that allowance for doubtful accounts reduces theoverall accounts receivable account, not a specific accountsreceivable assigned to a customer. Because it is an estimation, itmeans the exact account that is (or will become) uncollectible isnot yet known. Below is an example that demonstrates how the allowance for doubtful accounts works.

A bad debt expense is a financial transaction that you record in your books to account for any bad debts your business has given up on collecting. When you finally give up on collecting a debt (usually it’ll be in the form of a receivable account) and decide to remove it from your company’s accounts, you need to do so by recording an expense. Trade credit insurance protects your business from non-payment of commercial debt, making sure invoices are paid, and allowing you to reliably manage the dummy commercial and political risks of trade beyond your control.
It protects your capital, maintains your cash flows, and—most importantly—secures your earnings against defaults. When compared to self-insurnace, TCI provides you with a safer, more strategic accounts receivable management option. To break it down further, take a look at how both approaches compare for various aspects of your business. However, many in the financial industry avoid using this calculation method because of the length of time that can elapse between a sale and the determination that a debt is uncollectible.
Therefore, the allowance is created mainly so the expense can be recorded in the same period revenue is earned. For example, a company has $70,000 of accounts receivable less than 30 days outstanding and $30,000 of accounts receivable more than 30 days outstanding. Based on previous experience, 1% of accounts receivable less than 30 days old will be uncollectible, and 4% of those accounts receivable at least 30 days old will be uncollectible. The outstanding balance of $2,000 that Craft did not repay willremain as bad debt.
Doubtful accounts are considered to be a contra account, meaning an account that reflects a zero or credit balance. In other words, if an amount is added to the “Allowance for Doubtful social security Accounts” line item, that amount is always a deduction. In some cases, you may write off the money a customer owed you in your books only for them to come back and pay you.